Truffles
TRUFFLE IS THE NAME COMMONLY USED FOR HYPOGEAL FUNGUS, BELONGING TO THE TUBER GENUS AND CONSEQUENTLY TO THE TUBERACEAE FAMILY, A CLASS OF ASCOMYCETES
Being a hypogeal fungus, the truffle grows and matures in the earth below and alongside the roots of certain types of trees, especially oaks and holm oaks, with which the fungus establishes a symbiotic relationship, known as mycorrhizal, through which the truffles produce the much-prized sporocarp.


Truffles
TRUFFLE IS THE NAME COMMONLY USED FOR HYPOGEAL FUNGUS, BELONGING TO THE TUBER GENUS AND CONSEQUENTLY TO THE TUBERACEAE FAMILY, A CLASS OF ASCOMYCETES
Being a hypogeal fungus, the truffle grows and matures in the earth below and alongside the roots of certain types of trees, especially oaks and holm oaks, with which the fungus establishes a symbiotic relationship, known as mycorrhizal, through which the truffles produce the much-prized sporocarp.
Urbani Truffles,
True Jewels of Nature
Different types of truffle are identified by the shape of the peridium, the gleba, the asci and the spores.
80% of a truffle is made of water, while the remaining 20% comes from ash, total nitrogen, non-protein nitrogen, proteins, lipids, soluble carbohydrates and dietary fibre.
Truffles are best stored wrapped in absorbent paper, placed inside a plastic or glass container placed in the lower section of a fridge (0 to 4 degrees centigrade) for up to two or three days.
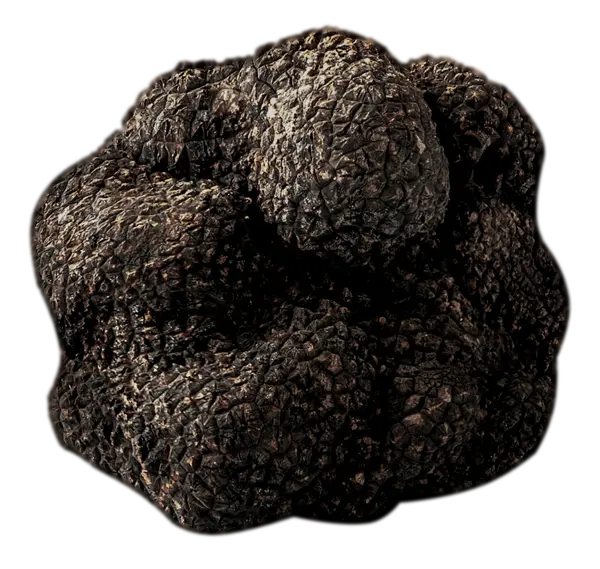

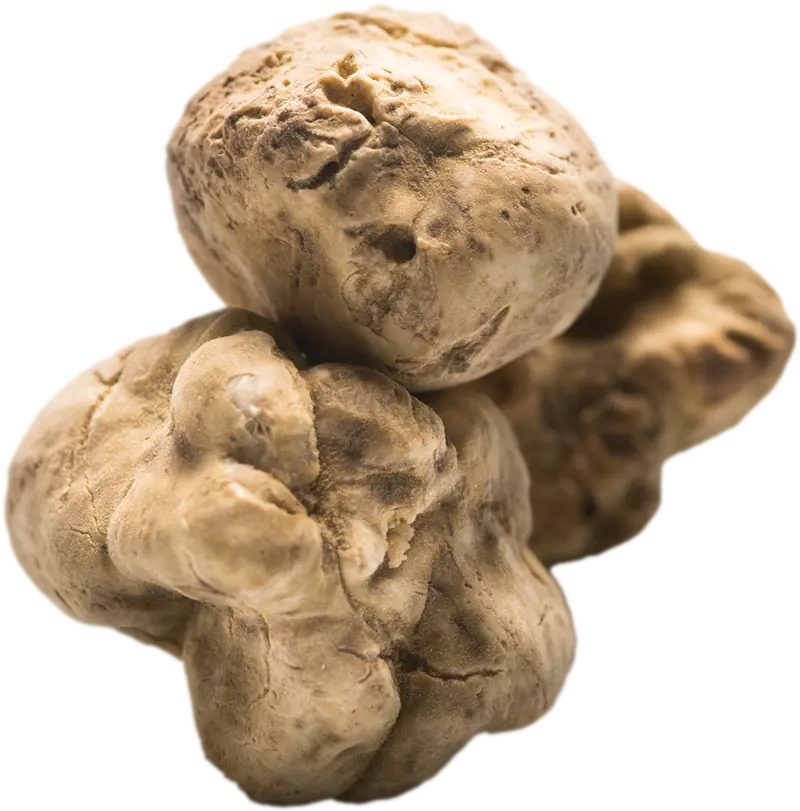
Types of truffle
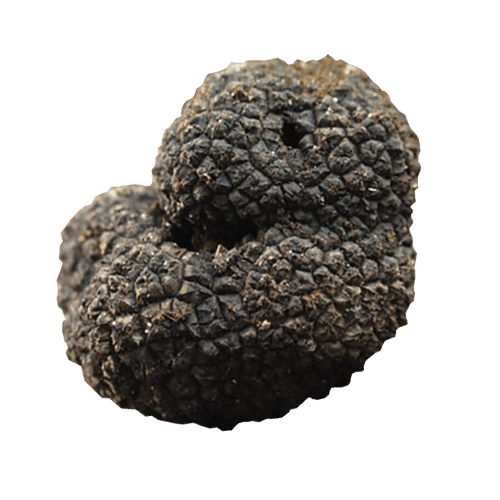

Bagnoli Truffle
Tuber Mesentericum Vittadini
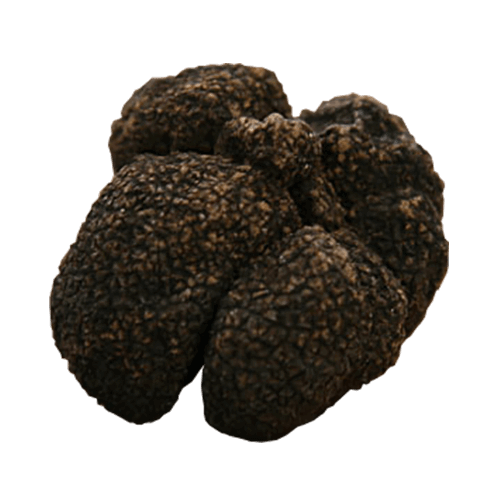

Moscato Truffle
Tuber Brumale Moschatum De Ferry
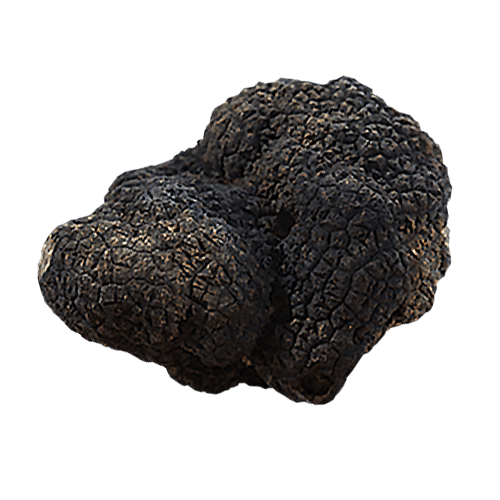

Uncinatum Truffle
Tuber Uncinatum Chatin
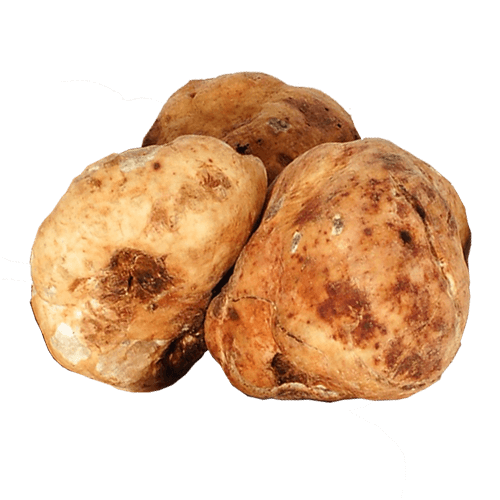

Bianchetto Truffle
Tuber Albidum Pico
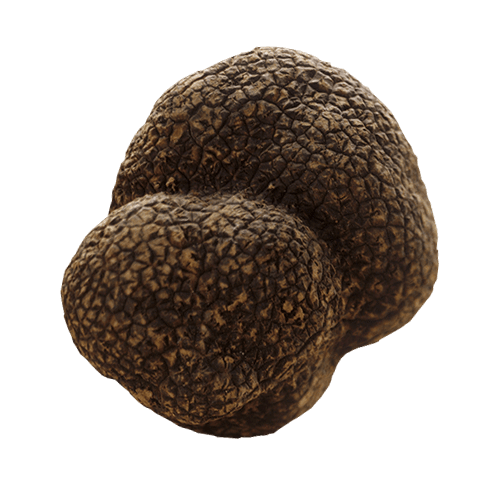

Black Summer Truffle
Tuber Aestivum Vittadini
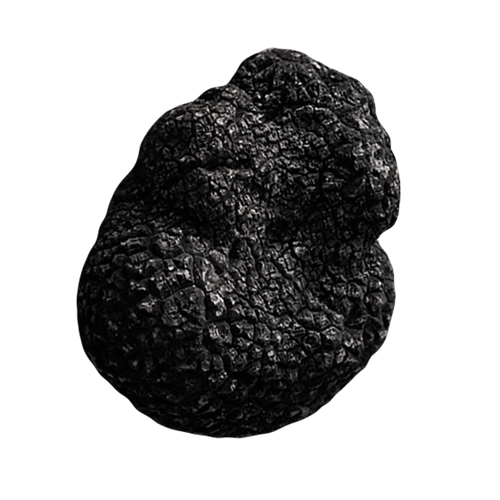

Black Winter Truffle
Tuber Brumale Vittadini
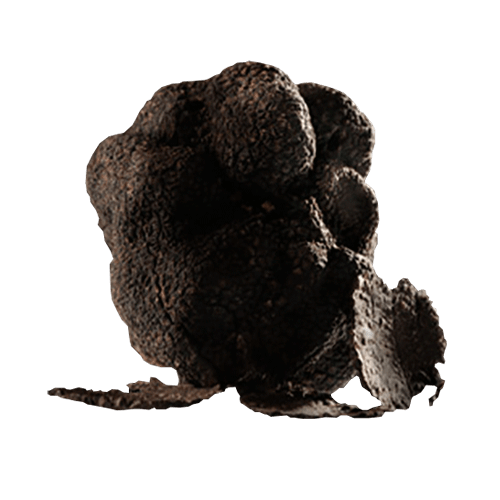

Fine Black Truffle
Tuber Melanosporum Vittadini
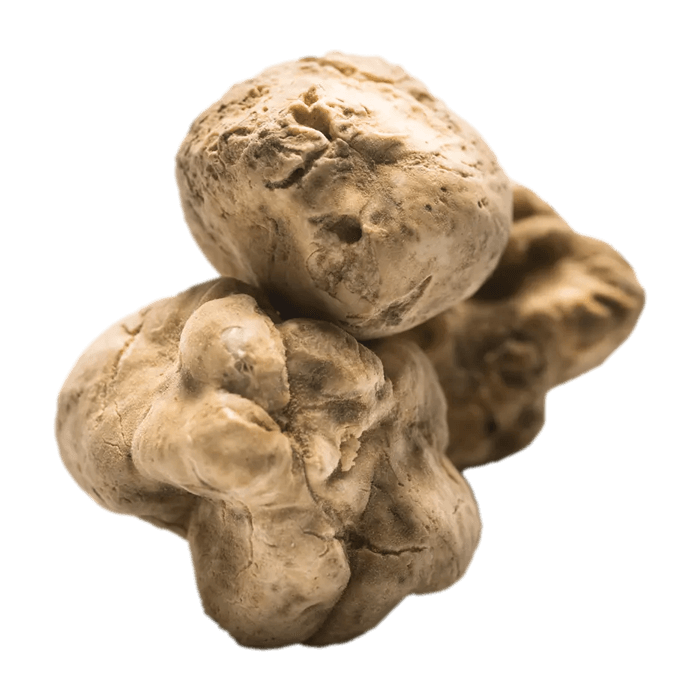

White Truffle
Tuber Magnatum Pico



